Growing apple trees from seed is an exciting project for gardeners and fruit lovers alike. While most commercial apple trees are grown using grafting techniques, there’s something special about starting from scratch with a single apple seed. In this article, we’ll explore how to germinate apple seeds, the challenges you might face, and why growing apples from seed might not always be the best option. We’ll also discuss how new apple varieties are developed, and provide a step-by-step guide for successfully planting apple seeds. Planting Apple Trees from Seed
How Do You Germinate Apple Seeds?
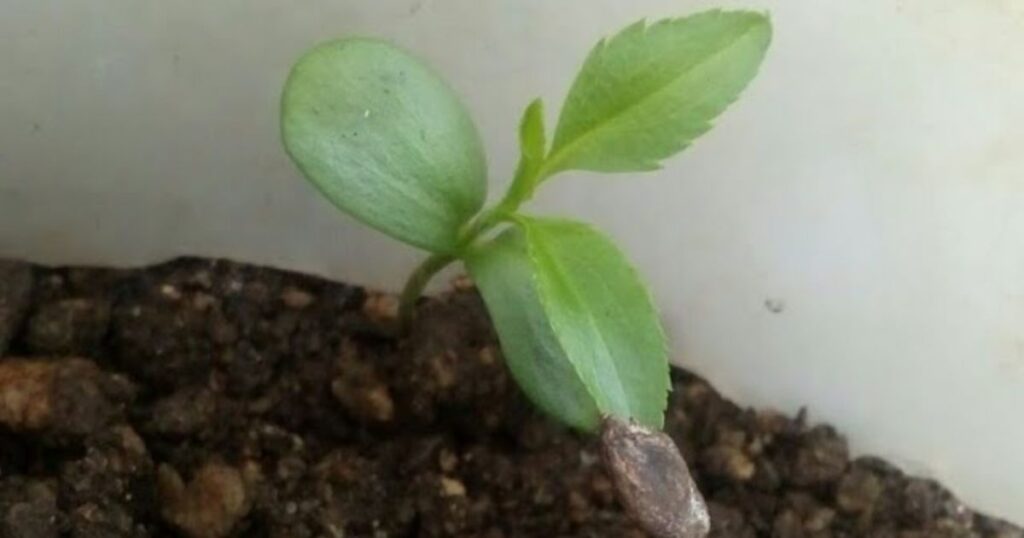

The Stratification Process for Apple Seeds
To germinate apple seeds, you need to mimic the natural conditions that seeds experience in the wild. In nature, apple seeds undergo a period of cold temperatures, which helps them break dormancy and begin growing. This process is known as stratification.
Here’s a step-by-step guide for stratifying apple seeds at home:
Collect seeds from ripe apples and clean off any remaining fruit pulp.
Place the seeds in a moist paper towel. Fold the towel over to cover the seeds completely.
Seal the paper towel in a plastic bag and store it in the refrigerator for at least 6-8 weeks.
Check the seeds periodically for signs of germination, which can occur during the stratification period.
This cold treatment helps increase the chances of successful apple seed germination.
Common Germination Problems
Even with stratification, not all seeds may germinate. Some common problems include:
- Inadequate stratification: If the seeds aren’t kept cold for long enough, they may not sprout.
- Mold growth: Excess moisture or improper storage can lead to mold, which kills seeds.
- Non-viable seeds: Some apple seeds simply won’t germinate due to genetic factors.
Why Not Grow Apples from Seed?
Genetic Mutations in Apple Varieties Planting Apple Trees from Seed
One of the biggest challenges when growing apple trees from seed is that you likely won’t get the same variety as the parent tree. Apple trees exhibit genetic diversity, meaning that seeds contain a mix of genes from both parent trees. This can result in trees that produce fruit with entirely different characteristics—sometimes with unexpected results. While this can occasionally lead to discovering a new apple variety, it often leads to less desirable fruit.
Why New Varieties Are Rarely Grown from Seed
Most new apple varieties are created through controlled crossbreeding and grafting techniques. For example, horticulturalists carefully select two parent apple trees with desired traits and graft branches from one onto the rootstock of another. This process ensures the resulting tree produces apples with the exact traits they want. Growing from seed, however, doesn’t provide this control.
How Do You Get New Trees Then?
Most new apple trees are propagated using grafting techniques. Here’s how it works:
- Grafting involves taking a cutting (scion) from a mature apple tree and attaching it to a rootstock.
- The rootstock is often a dwarf or disease-resistant variety, which provides a strong foundation for the apple tree.
- The scion grows into a new tree that produces the same type of fruit as the original tree.
This method guarantees that the tree will bear fruit identical to the parent tree. Commercial growers use this technique to ensure consistency in apple varieties like Gala, Fuji, and Honeycrisp.
Can I Grow an Apple from Seed?

Yes, you can grow an apple tree from seed, but there are some downsides to consider. The apples you get may be very different from the ones you started with. If you’re aiming for a specific type of apple, growing from seed might lead to disappointment. However, growing from seed can be an enjoyable experiment, and it’s a great way to learn about apple tree cultivation.
What is the Downside of Growing Apples from Pips?
The biggest downside is unpredictability. When you grow apples from pips (the seeds found in the core of the fruit), you have no control over the variety of apples the tree will produce. In addition, growing an apple tree from seed takes much longer to produce fruit—typically around 7 to 10 years. In comparison, grafted trees often produce fruit within just a few years.
How Big Will My Apple Tree Grow?
Apple trees can grow to different sizes depending on the variety and rootstock. For instance:
- Standard apple trees: Can grow up to 20-30 feet tall.
- Dwarf apple trees: Typically reach about 8-10 feet in height, making them easier to manage and ideal for smaller spaces.
- Semi-dwarf trees: Generally grow to around 12-15 feet.
The choice of rootstock will also influence how large your tree will grow.
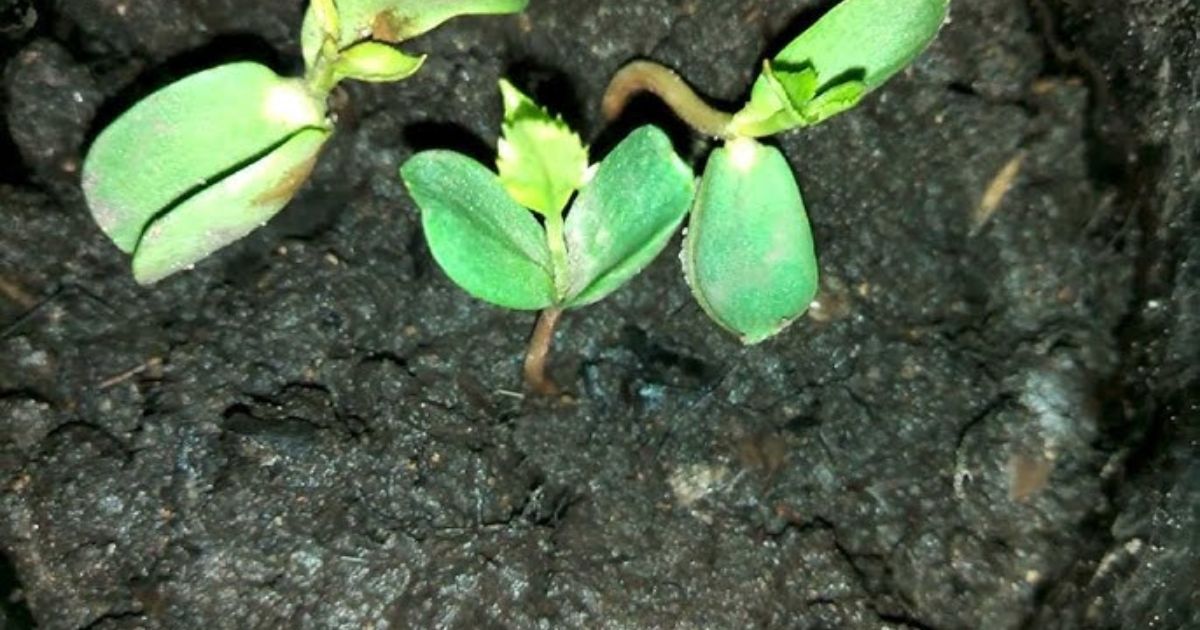
How to Sow Apple Seeds
Sowing apple seeds is a relatively simple process once they’ve been stratified. Here’s how:
Prepare a pot or garden bed with well-draining soil.
Plant the seeds about ½ inch deep in the soil, keeping them spaced out to allow for growth.
Water the seeds thoroughly and place the pot in a sunny spot.
Be patient! It may take a few weeks for the seeds to sprout, so keep the soil moist but not waterlogged.
How to Prepare Apple Seeds for Planting
Before planting, it’s important to prepare your seeds to increase the likelihood of successful germination. Follow these steps:
- Clean the seeds by removing any fruit pulp and drying them gently.
- Stratify the seeds by chilling them for 6-8 weeks in the refrigerator (as outlined earlier).
- Inspect the seeds periodically to ensure they don’t dry out or develop mold.
How to Plant Apple Seeds

Once your seeds have germinated, here’s how to plant them:
Choose the right location: Apple trees need full sunlight, so pick a spot that gets at least 6 hours of direct light.
Dig a hole that’s large enough for the seedling’s root system—typically 2-3 inches deep for a seedling.
Plant the seedling carefully, making sure the roots are spread out evenly.
Water the tree regularly and protect it from pests and extreme weather conditions during the early stages.
Table: Apple Tree Pollination Methods
| Pollination Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Self-Pollination | Some apple varieties can pollinate themselves but may still benefit from cross-pollination. |
| Cross-Pollination | Requires pollen from another apple variety for successful fruit development. |
| Pollination by Bees | Bees play a critical role in transferring pollen between apple blossoms. |
Fruit Tree Maintenance Tips
Once your apple tree has been planted, ongoing care is essential for healthy growth and fruit production:
- Prune the tree annually to remove dead or diseased branches.
- Monitor for pests such as aphids and codling moths, which can harm fruit development.
- Apply organic farming techniques like mulching and composting to maintain soil health.
- Be on the lookout for diseases such as fire blight, which can damage trees and reduce yields.
Apple Tree Cultivation Strategies for Success
- Select disease-resistant varieties to minimize the risk of infection.
- Use dwarf or semi-dwarf rootstock for easier tree management.
- Incorporate pollinator-friendly plants in your orchard to encourage bees and other beneficial insects.
By following these steps and understanding the intricacies of apple seed germination, you’ll be well on your way to cultivating your very own apple tree. Whether you choose to grow your tree from seed or through grafting, the joy of harvesting homegrown apples is well worth the effort
Conclusion
Growing apple trees from seeds can be a fun and rewarding process, but it comes with its challenges. From understanding apple seed germination and grafting techniques to dealing with diseases like fire blight, there’s a lot to consider. However, with the right preparation and care, you can grow your apple tree, potentially yielding delicious fruit in just a few years.

I am Alexander James, a seasoned professional with 4 years of expertise, brings passion and skill to every project. Elevate your experience with my knowledge and creativity.


![Hollyhock Seeds: The Complete Guide to Success [2024]](https://seederabout.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Hollyhock-Seeds-The-Complete-Guide-to-Success-2024-300x157.jpg)





