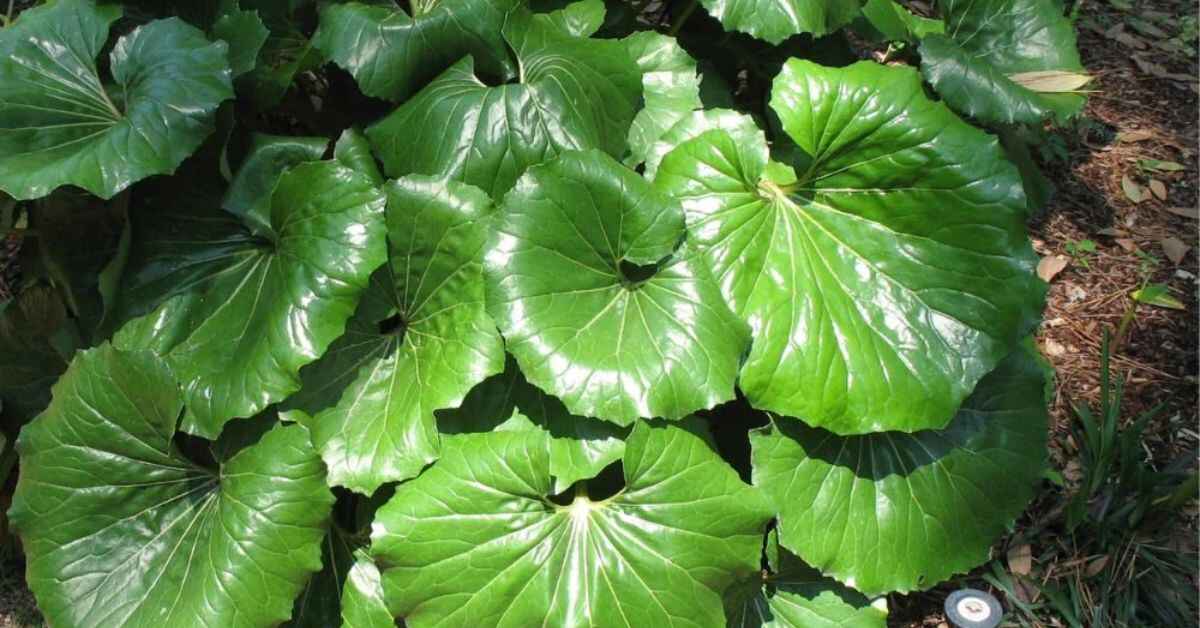
The giant leopard plant (Farfugium japonicum), also known as Ligularia dentata, is a striking, shade-loving perennial known for its bold foliage and bright, yellow, daisy-like flowers. This large-leafed perennial is prized in gardens for its tropical-looking leaves, making it a standout feature in any landscape. Whether you’re planning to add this bold garden plant to a shady spot in your yard or use it as a container plant indoors, this comprehensive guide will cover everything you need to know about growing and caring for the giant leopard plant.
What is a Giant Leopard Plant?
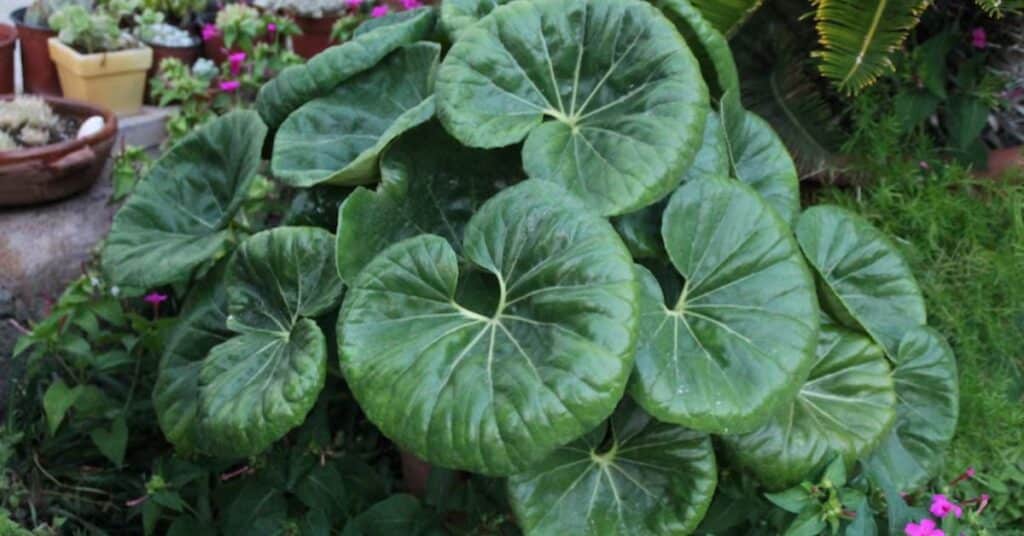

The giant leopard plant is a member of the Asteraceae family and is native to Japan and Korea. It is widely appreciated for its broad leaves, which can reach up to 12 inches in diameter, and its eye-catching foliage. The large, glossy leaves are often deep green, but some varieties display spotted patterns that resemble a leopard’s coat, giving the plant its name.
Besides its beautiful leaves, the giant leopard plant blooms in late summer to fall, producing clusters of yellow daisy-like flowers that rise above the foliage on tall stems. These flowers add a cheerful splash of color to shady garden areas, where bright flowers are often hard to come by.
Plant Height and Spread:
- Typically, the giant leopard plant grows to a height of 2 to 4 feet, with a spread of 3 to 5 feet, making it an excellent choice for filling in large, shaded garden spaces.
Fun Fact: The giant leopard plant is also commonly known as the tractor seat plant, due to the shape of its large, rounded leaves.
Ideal Growing Conditions for the Giant Leopard Plant
Light Requirements
The giant leopard plant thrives in partial to full shade, making it a go-to choice for shade-loving plants in gardens that don’t receive much direct sunlight. While it can tolerate a small amount of morning sun, too much exposure to direct sunlight, especially during the hottest parts of the day, can cause the leaves to scorch or wilt.
If you’re growing the plant indoors, place it in a spot that gets plenty of indirect light but is protected from harsh afternoon sun.
Soil Preferences
One of the most important requirements for growing the giant leopard plant successfully is soil. It prefers moist, well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. The ideal pH level for the soil is slightly acidic to neutral, around 6.0 to 7.0.
Moist soil requirement:
- Consistently moist soil is crucial for this water-loving plant, as it does not tolerate drought well. Mulching around the base of the plant can help retain moisture, especially during hot weather.
If your garden soil has poor drainage, consider adding organic matter like compost or using raised beds to improve the conditions for your wetland garden plants.
Watering Schedule
The giant leopard plant enjoys moist soil, so it’s important to water it regularly. However, the key is balance: too much water can cause root rot, while too little can lead to wilting.
- Watering tips: Keep the soil consistently moist, but avoid letting the plant sit in standing water. Deep watering once a week is usually sufficient, especially if mulch is used to help retain moisture.
Temperature and Humidity
This cold-hardy perennial can withstand a variety of conditions, but it prefers cooler climates. It does well in USDA Hardiness Zones 7-10 and can survive mild frosts. In colder climates, it may die back during the winter but will return in the spring.
Humidity: The giant leopard plant thrives in areas with higher humidity. If growing indoors, you can boost humidity around the plant by misting it regularly or using a humidifier.
Plant Height and Spread
As mentioned, the giant leopard plant can grow up to 4 feet tall and spread 3 to 5 feet wide. This makes it an excellent plant for filling larger spaces in a partial shade garden. Its lush, tropical-looking leaves create a dramatic visual impact, making it a great choice for garden border plants or as a focal point in a shaded bed.
Azolla Plant Seeds: A Comprehensive Guide to Growing, Using, and Maximizing Azolla Cultivation
How to Plant and Transplant the Giant Leopard Plant

Planting Time
The best time to plant the giant leopard plant is in the spring or fall when temperatures are cooler, and the plant can establish its root system before the heat of summer or the cold of winter.
Planting Instructions
Choose the right spot: Select a location with partial to full shade and moist, well-draining soil.
Prepare the soil: Loosen the soil to a depth of 12-15 inches and mix in organic matter like compost or peat moss to improve soil texture and nutrient content.
Plant the leopard plant: Dig a hole twice as wide as the root ball but no deeper. Place the plant in the hole, ensuring the top of the root ball is level with the soil surface.
Water thoroughly: After planting, water deeply to help settle the soil around the roots.
Transplanting Tips
If you need to move your giant leopard plant or divide it to propagate new plants, it’s best to do so in the spring or early fall. Ensure you dig deep enough to avoid damaging the root system and replant in moist soil immediately after transplanting.
Caring for the Giant Leopard Plant
Pruning and Maintenance
The giant leopard plant is a low-maintenance plant, but occasional care will keep it looking its best.
- Pruning: Remove any dead or damaged leaves throughout the growing season to maintain a tidy appearance. In late winter or early spring, you can cut back any remaining foliage to make way for new growth.
- Fertilizing: Apply a balanced, slow-release fertilizer in the spring to promote healthy growth. Organic fertilizers like compost or well-rotted manure can also be beneficial.
Pest and Disease Management
One of the advantages of the giant leopard plant is that it’s a deer-resistant plant, making it a great choice for gardens prone to deer browsing.
However, it can be susceptible to slugs and snails, which are attracted to its large, tender leaves. To manage these pests, use natural remedies like crushed eggshells or copper tape around the base of the plant.
Landscaping with the Giant Leopard Plant
The giant leopard plant makes a stunning addition to any shade garden, with its ornamental foliage and bold leaves providing year-round interest.
Companion Plants for Ligularia
For a harmonious look, pair the giant leopard plant with other shade-loving plants that enjoy similar conditions. Good companion plants include:
- Hostas: Their variegated foliage complements the dark green leaves of the leopard plant.
- Ferns: Add a delicate texture that contrasts beautifully with the bold, broad leaves of the leopard plant.
- Astilbes: Their feathery flowers provide a soft, colorful contrast to the plant’s large leaves.
Using Giant Leopard Plant in Garden Design
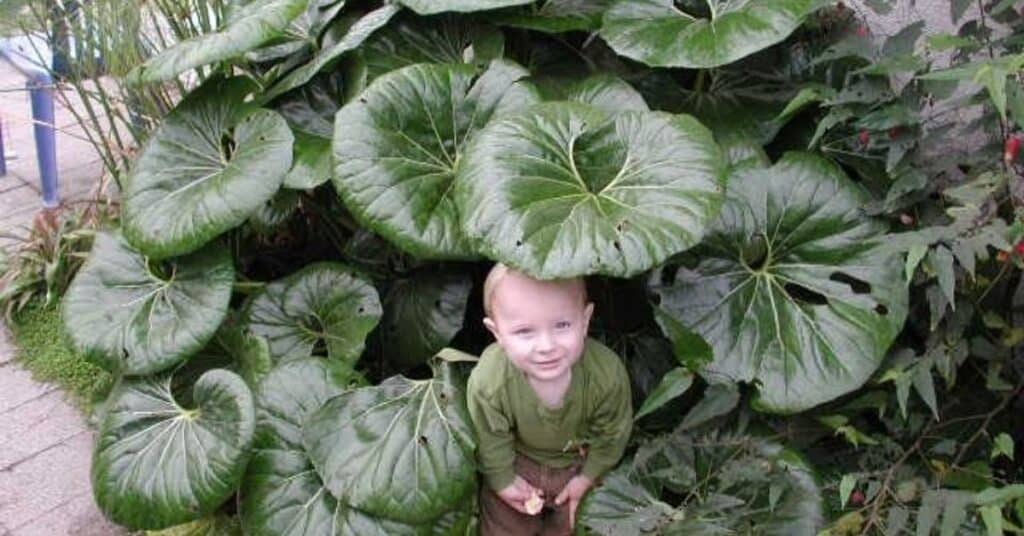

Whether you’re creating a wetland garden or looking for a dramatic plant for a shady corner, the giant leopard plant is a versatile choice. Its tropical-looking leaves and bright yellow flowers make it ideal for:
- Garden borders: Plant it along the edge of shaded garden beds.
- Water features: Since it’s a water-loving plant, it thrives near ponds or in areas with high moisture.
- Container gardening: Its bold foliage looks fantastic in large containers, especially on shady patios or balconies.
Conclusion
The giant leopard plant is a striking, low-maintenance addition to any shade garden. With its large, tropical-looking leaves, yellow daisy-like flowers, and moist soil requirement, it’s the perfect choice for gardeners looking to create a lush, tropical feel in cooler climates. Whether you’re planting it as a focal point or as part of a larger design, its unique appearance and deer-resistant nature make it a valuable addition to your landscape.
By providing the right growing conditions and a little care, this cold-hardy perennial will reward you with bold foliage and bright flowers for years to come.

I am Alexander James, a seasoned professional with 4 years of expertise, brings passion and skill to every project. Elevate your experience with my knowledge and creativity.


![Hollyhock Seeds: The Complete Guide to Success [2024]](https://seederabout.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Hollyhock-Seeds-The-Complete-Guide-to-Success-2024-300x157.jpg)





