Moringa, often called the “Miracle Tree” or “Drumstick Tree,” has been valued for centuries for its incredible nutritional and medicinal benefits. It is a fast-growing superfood tree that thrives in dry climates, making it ideal for organic gardening. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through Moringa cultivation, from preparing the soil to planting Moringa seeds, transplanting, watering, and caring for the tree. Whether you’re aiming to grow Moringa for its nutrient-rich leaves, medicinal uses, or simply to have a drought-resistant plant in your garden, you’ll find everything you need to get started.
Understanding Moringa: The Miracle Tree
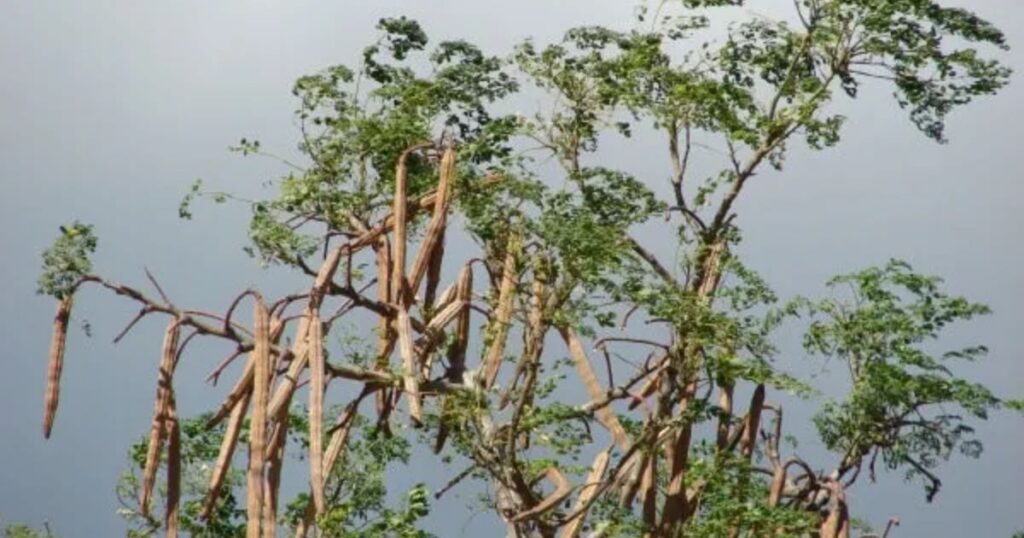

What is Moringa?
Moringa Oleifera, commonly known as the Drumstick Tree, is native to India but thrives in tropical and subtropical regions across the globe. This tropical plant growth is prized for its nutritious super green leaves, which are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Moringa is considered a superfood due to its high content of calcium, potassium, vitamin C, and protein.
Moringa has been dubbed the “Miracle Tree” for its ability to provide an array of health benefits, from reducing inflammation to purifying water. Many parts of the plant are useful, including the leaves, seeds, and pods. In addition to being a nutrient-rich tree, Moringa is known for its drought resistance, making it a sustainable option in dry regions.
Why Grow Moringa from Seeds?
Growing Moringa from seeds is not only cost-effective but also ensures a robust and strong root system. Moringa seeds germination leads to a resilient tree that can withstand tough environmental conditions. By planting Moringa from seeds, you’re investing in a tree that can live up to 20 years or more with the right care.
Preparing the Right Soil for Moringa Seeds
Soil Composition and Type
Moringa thrives in well-draining soils. The key to successful Moringa cultivation lies in soil that is not too heavy or waterlogged. A loamy or sandy soil with a pH level between 6.3 and 7.0 is ideal. This will ensure the plant’s roots can expand freely, allowing for quicker growth.
The Complete Guide to Growing and Caring for the Giant Leopard Plant
Ideal Soil Characteristics for Moringa Seeds
| Soil Type | pH Level | Drainage | Nutrients |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sandy/Loamy Soil | 6.3 – 7.0 | Well-draining | Compost-rich for nutrients |
Soil Amendments
Before planting, enrich the soil with organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure. This boosts nutrient levels and ensures a healthier tree. If your soil has a high clay content, consider mixing in some sand to improve drainage, as Moringa roots are prone to rot in waterlogged conditions.
- Tip: Avoid heavy clay soils or areas prone to flooding. You can use raised beds to mitigate these issues.
Common Soil Problems to Avoid
- Compacted Soil: Break up the top layer of soil before planting to ensure proper aeration.
- Poor Drainage: If water pools in the area where you’re planting, use raised beds or amend the soil with sand and organic material.
Choosing and Planting Moringa Seeds
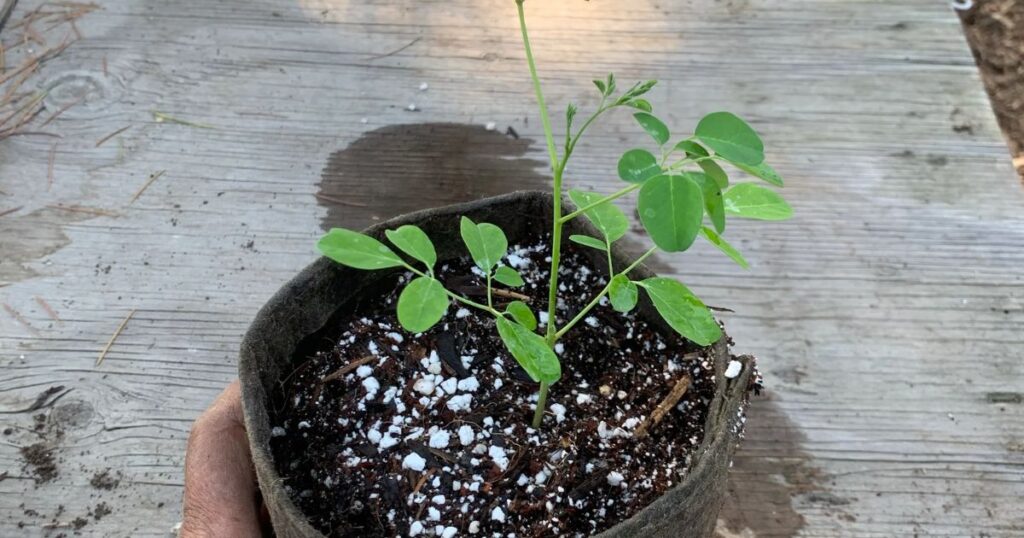

Seed Selection
Choosing high-quality seeds is essential for successful Moringa seeds germination. Look for mature seeds that are dark brown in color with a hard outer shell. Fresh seeds usually offer better germination rates than older seeds. You can source Moringa seeds from online stores, garden centers, or local farmers.
Germination Process
For optimal germination, soak the Moringa seeds in water for 24 hours before planting. This helps to soften the hard outer shell and encourages faster sprouting. After soaking, plant the seeds directly into the soil or a container.
- Planting Depth: About ½ inch deep.
- Spacing: Seeds should be spaced 1–2 feet apart to allow ample room for growth.
Germination typically takes 7-14 days, depending on soil warmth and moisture.
Direct Sowing vs. Seed Starting Indoors
You can plant Moringa seeds directly in the ground if you live in a warm, frost-free climate. However, if you live in a colder region, it’s better to start the seeds indoors and transplant them outside after the last frost.
- Direct Sowing Pros: No transplant shock, quicker adaptation to the environment.
- Indoor Seed Starting Pros: Greater control over conditions like temperature and moisture.
Watering Moringa Seeds Properly
Optimal Watering Schedule
Although Moringa is drought-tolerant, young seedlings require consistent moisture for healthy growth. The trick is to strike a balance between keeping the soil moist and avoiding waterlogging. After germination, water the seedlings 2-3 times per week.
Watering Methods
- Drip irrigation is ideal for Moringa water needs, ensuring even moisture distribution without over-wetting the soil.
- Hand-watering is sufficient if you have a small garden. Ensure the top few inches of soil remain moist but not soaked.
Signs of overwatering include yellowing leaves and stunted growth, while underwatering may cause wilting and slow growth.
Transplanting Moringa Seedlings (If Starting Indoors)
When to Transplant Moringa Seedlings Outdoors
If you’ve started your seeds indoors, wait until they are about 12-18 inches tall before transplanting. Ensure the outdoor temperature is consistently above 70°F, as Moringa thrives in warm climates.
Transplanting Techniques
- Prepare the site by digging a hole twice the width of the root ball.
- Water the seedlings thoroughly before transplanting to ease the transition.
- Place the plant in the hole, fill it with soil, and press it gently around the base.
- Tip: Water the newly transplanted Moringa trees deeply and regularly for the first two weeks to help establish the root system.
Caring for and Maintaining Moringa Trees
Sunlight and Temperature Needs
Moringa requires full sun to thrive. It can tolerate temperatures up to 110°F but does not do well in frosty conditions. Ensure the tree receives 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily.
Pruning Tips
Regular pruning is essential to encourage bushier growth and improve leaf production. Prune the top branches once the tree reaches about 3-4 feet tall to promote lateral branching.
- Tip: Cut back older, woody stems in the dry season to stimulate new growth.
Organic Moringa Gardening: Pest and Disease Control
Moringa is relatively pest-resistant, but certain pests like aphids or caterpillars may occasionally attack the tree. Use organic pest control methods like neem oil sprays or introduce beneficial insects to the garden.
Harvesting Moringa: From Seeds to Leaves
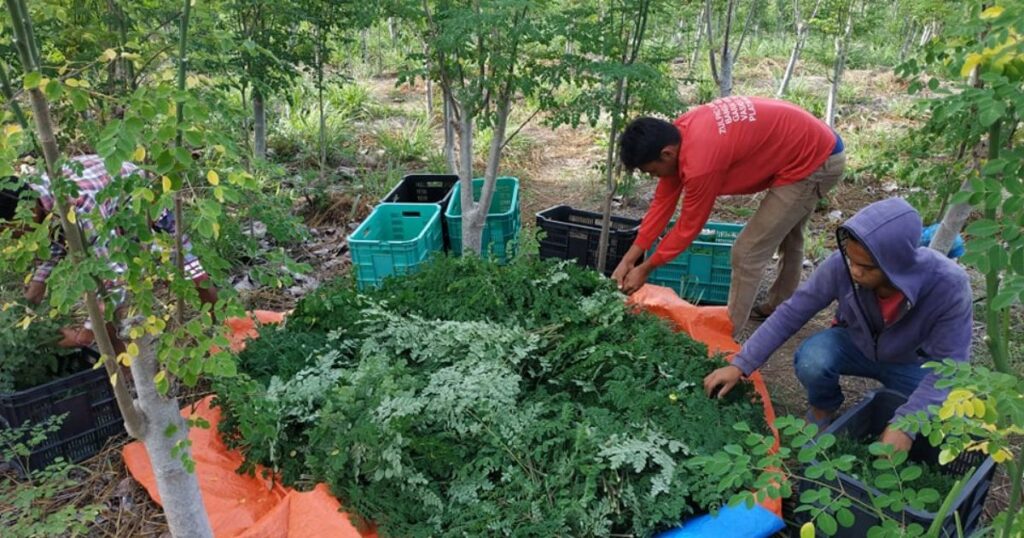

Harvesting Moringa Leaves
Moringa leaves can be harvested once the tree reaches about 4 feet in height. Regular harvesting encourages continuous leaf production. For maximum nutrients, harvest leaves during the cooler parts of the day, such as early morning or late afternoon.
- Tip: Dry Moringa leaves in a shaded, well-ventilated area to preserve their nutrients. Once dried, they can be ground into powder and used in smoothies or soups.
Harvesting Moringa Seeds and Pods
Moringa seeds can be harvested once the pods turn brown and dry on the tree. Drumstick plant care includes checking pods regularly during the harvesting season, which typically occurs between six and eight months after planting.
- Tip: Store seeds in a cool, dry place to maintain their viability for future planting.
Moringa’s Versatility: Medicinal and Practical Uses
Nutritional and Medicinal Uses
Moringa leaves are considered a nutritious super green, full of vitamins A, C, and E, as well as calcium, potassium, and protein. The leaves have anti-inflammatory properties, making them popular in traditional medicine. Consuming Moringa leaves can boost immunity, reduce blood sugar levels, and improve digestive health.
- Fact: Moringa has been used to treat malnutrition in developing countries due to its dense nutritional profile.
Water Purification with Moringa
One lesser-known use of Moringa seeds is their ability to purify water. Crushed Moringa seeds act as a natural coagulant, removing impurities from water and making it safe for drinking.
Conclusion
By growing Moringa from seeds, you’re not just cultivating a tree; you’re planting a fast-growing superfood tree with incredible miracle tree benefits. From its nutrient-rich leaves to its drought resistance and ability to thrive in dry climate gardening, Moringa is a versatile and valuable addition to any garden. With proper care, including understanding Moringa soil requirements, transplanting techniques, and harvesting methods, you’ll be rewarded with a sustainable, long-lasting source of nutrition and natural health benefits.

I am Alexander James, a seasoned professional with 4 years of expertise, brings passion and skill to every project. Elevate your experience with my knowledge and creativity.


![Hollyhock Seeds: The Complete Guide to Success [2024]](https://seederabout.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Hollyhock-Seeds-The-Complete-Guide-to-Success-2024-300x157.jpg)





